Table of Contents
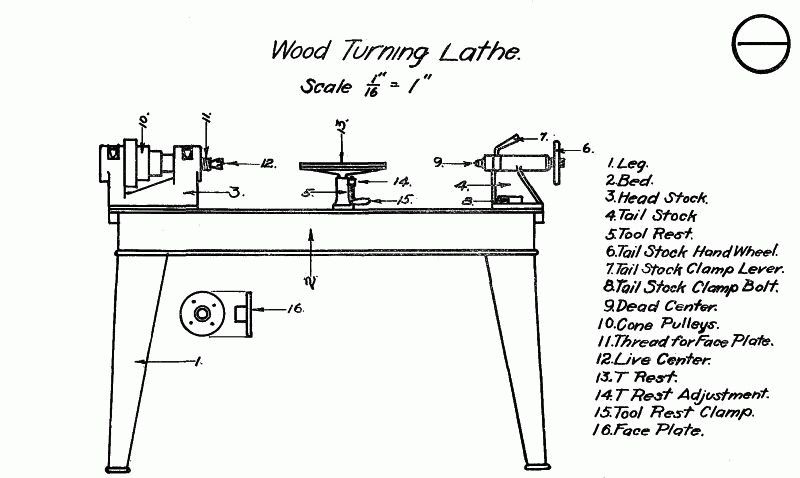
A wood turning lathe consists of the headstock, tailstock, bed, tool rest, and motor. These parts work together to shape wood.
Wood turning lathes are essential tools for woodworking enthusiasts and professionals. The headstock houses the motor and spindle, providing rotational force. The tailstock supports the other end of the workpiece, ensuring stability. The bed is the foundation, holding the headstock and tailstock in place.
The tool rest allows for precise control of cutting tools, enhancing accuracy. Proper maintenance of these parts ensures smooth operation and longevity. Understanding each component’s function helps in making informed purchasing and maintenance decisions. This knowledge is crucial for achieving desired results in woodturning projects, whether for decorative items or functional pieces.
Introduction To Wood Turning Lathes
Wood turning lathes are essential tools for woodworkers. They shape wood into beautiful and functional objects. From bowls to table legs, lathes make the work easy and precise.
The Role Of Lathes In Woodworking
Lathes hold and spin wood while you shape it. They allow for controlled and precise carving. You can create symmetrical shapes with ease. Lathes are important for both beginners and experts. They help in making furniture, art, and everyday items.
Basic Anatomy Of A Lathe
Understanding the parts of a lathe is crucial. Here is a table to help you learn:
| Part | Description |
|---|---|
| Headstock | Holds the motor and spindle. It spins the wood. |
| Tailstock | Supports the other end of the wood. It can be adjusted. |
| Tool Rest | Supports the cutting tools. It can be moved as needed. |
| Bed | The base of the lathe. It holds all parts together. |
| Spindle | Rotates the wood. It is powered by the motor. |
| Chuck | Holds the wood securely. It can be tightened or loosened. |
The Bed: Foundation Of Stability
The bed is the foundation of stability in wood turning lathes. It holds all other components together. A sturdy bed ensures smooth, precise woodturning. Understanding its parts and maintenance can enhance your woodworking experience.
Materials And Design
The bed is typically made from cast iron. Cast iron provides stability and vibration resistance. Some beds are made from steel or aluminum. These materials offer different benefits. Steel beds are durable and strong. Aluminum beds are lightweight and portable.
The bed’s design affects its performance. Some beds have a flat surface. Others have a V-shaped or T-shaped design. These shapes help in aligning the lathe components. The length of the bed also matters. A longer bed allows for turning larger pieces. Shorter beds are compact and suitable for small workshops.
Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance keeps the bed in good condition. Clean the bed after each use. Remove wood dust and shavings. Use a soft brush or cloth.
Check for rust and corrosion. Apply a light coat of oil to prevent rust. Inspect for any cracks or damages. Tighten any loose bolts or screws.
Level the bed for accurate turning. Use a spirit level to check the alignment. Adjust the feet if necessary. Ensure the bed is stable and does not wobble.
| Material | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Cast Iron | High stability and vibration resistance |
| Steel | Durable and strong |
| Aluminum | Lightweight and portable |
- Clean the bed regularly
- Check for rust and apply oil
- Inspect for cracks and damages
- Level the bed for accurate turning
Headstock: The Powerhouse
The headstock is the heart of a wood turning lathe. It holds the spindle and drive mechanisms that power the lathe. This section is crucial for efficient woodturning.
Drive Mechanisms Explained
The drive mechanism in the headstock transfers power to the spindle. Here are the common types:
- Belt Drive: Uses belts to transfer power. It is quiet and smooth.
- Direct Drive: The motor connects directly to the spindle. It offers high efficiency.
- Variable Speed: Allows speed adjustment. Perfect for different wood types.
Choosing The Right Spindle
Selecting the right spindle is important for your lathe’s performance. Consider these factors:
| Factor | Details |
|---|---|
| Size | Spindle size should match your lathe. Common sizes are 1″ x 8 TPI. |
| Material | Spindles are usually made of steel. Steel is durable and strong. |
| Thread | Check the thread type. It should fit your lathe’s accessories. |
The headstock is a key part of your wood turning lathe. Understand its drive mechanisms and choose the right spindle.
Credit: www.aroundthewoods.com
Tailstock: Support And Precision
The tailstock is a key component of any wood turning lathe. It provides support and ensures precision during the turning process. The tailstock holds the workpiece steady, allowing for accurate and safe woodturning.
Live Center Vs. Dead Center
The tailstock can use either a live center or a dead center. These are two different types of centers that hold the workpiece.
| Live Center | Dead Center |
|---|---|
| The live center rotates with the workpiece. | The dead center stays stationary. |
| Reduces friction and heat. | Can cause friction and heat. |
| Suitable for high-speed turning. | Better for low-speed tasks. |
A live center is usually more versatile. A dead center is great for specific tasks where rotation is not needed.
Adjustments And Alignment
Proper adjustment and alignment of the tailstock are crucial for precision. Misalignment can cause inaccuracies and damage to the workpiece.
- Ensure the tailstock is parallel to the bed.
- Adjust the tailstock to match the center of the spindle.
- Lock the tailstock securely to prevent movement.
Check the alignment regularly to maintain precision. Use a ruler or alignment tool for accuracy.
Making these adjustments ensures your woodturning projects are precise and professional. This attention to detail enhances the quality of your work.
Tool Rest: Control And Safety
The tool rest is a key part of a wood turning lathe. It provides stability and control while turning. Proper use ensures your safety and the quality of your work. This section explains the types of tool rests and how to use them correctly.
Types Of Tool Rests
There are several types of tool rests available:
- Standard Tool Rest: This is the most common type. It is used for general turning tasks.
- Curved Tool Rest: This rest is ideal for bowl turning. It allows you to follow the curve of the bowl.
- Adjustable Tool Rest: This type offers flexibility. You can adjust it to various positions for different tasks.
- Modular Tool Rest: This rest has interchangeable parts. It lets you customize the setup based on your needs.
Proper Use And Positioning
Using the tool rest correctly is crucial for both safety and precision:
- Adjust the Height: The tool rest should be at or just below the center of the workpiece.
- Position Close: Place the tool rest as close to the workpiece as possible. This reduces the leverage on your tool, giving you better control.
- Maintain Distance: Keep a small gap, about 1/8 inch, between the tool rest and the workpiece. This prevents the tool from catching.
- Secure It: Ensure the tool rest is locked in place before starting. A loose tool rest can be dangerous.
Always check the tool rest for damage. Replace it if you find any cracks or wear. This simple check can prevent accidents and improve your turning quality.
By understanding the different types of tool rests and their proper use, you can turn wood safely and effectively. Happy turning!
Carriage And Saddle: Movement And Stability
The carriage and saddle are essential parts of a wood turning lathe. They ensure precise movement and stability during operations. Understanding their functionality and proper adjustment is crucial for smooth performance. This section will delve into these aspects, providing insights on how to maintain and optimize them.
Functionality And Adjustment
The carriage moves along the lathe bed, carrying the cutting tool. The saddle provides support and stability to the carriage. Proper adjustment of these parts ensures accurate and efficient wood turning. Regular checks and adjustments can prevent issues like vibration and misalignment.
Adjust the carriage using the handwheel or controls. Ensure it moves smoothly along the bed. Check the saddle for tightness and proper alignment. Use the adjustment screws to fine-tune its position. This maintains stability and prevents unwanted movement.
Ensuring Smooth Operation
Maintaining smooth operation of the carriage and saddle is vital. Lubricate the moving parts regularly. This reduces friction and wear. Clean the lathe bed and carriage rails to remove debris. This prevents blockages and keeps the parts moving freely.
Inspect the carriage and saddle for signs of wear or damage. Replace any worn or damaged parts promptly. Regular maintenance checks can extend the lifespan of your lathe. It also ensures consistent performance and precision in your wood turning projects.
Spindle: The Turning Point
The spindle is the heart of a wood turning lathe. It plays a crucial role. It holds and spins the wood piece. A good spindle ensures smooth and accurate turning.
Varieties And Selection
Choosing the right spindle is key. There are many types available. Each type serves a unique purpose.
- Threaded Spindles: These are common in most lathes. They hold chucks and faceplates.
- Morse Taper Spindles: These spindles are versatile. They can hold various tools.
- Cam Lock Spindles: These offer quick tool changes. They are efficient and time-saving.
Select a spindle based on your project needs. Consider the type of wood and the desired finish.
Care And Upkeep
Proper care extends the life of your spindle. Regular maintenance is essential.
- Lubrication: Keep the spindle well-lubricated. This ensures smooth operation.
- Cleaning: Remove dust and debris. Clean after each use.
- Inspection: Check for wear and tear. Replace parts as needed.
Follow these steps for a long-lasting spindle. A well-maintained spindle ensures better performance.
Motor And Drive System: Powering The Lathe
The motor and drive system are the heart of any wood turning lathe. They provide the necessary power to turn the wood smoothly and efficiently. Understanding these components helps in achieving precise and consistent results.
Electric Vs. Manual Drives
Electric drives are the most common in modern wood lathes. They offer consistent power and adjustable speed. This makes them ideal for detailed and complex projects.
Manual drives rely on human power. They are less common today but are still used for traditional woodturning. These drives offer a unique tactile experience and are often favored by hobbyists.
- Electric Drives:
- Consistent power
- Adjustable speed
- Ideal for complex projects
- Manual Drives:
- Human-powered
- Traditional method
- Preferred by hobbyists
Understanding Torque And Speed
Two critical factors in a lathe’s performance are torque and speed. Torque is the rotational force, while speed is how fast the lathe spins. Balancing these two ensures smooth and accurate woodturning.
High torque is essential for working with hard woods. It provides the force needed to cut through tough material. Low torque is better for soft woods and detailed work.
Speed settings are equally important. High speed is useful for roughing out shapes quickly. Low speed is ideal for finishing and detail work. Most electric lathes offer variable speed controls for flexibility.
| Factor | High Setting | Low Setting |
|---|---|---|
| Torque | Hard woods | Soft woods, detail work |
| Speed | Roughing shapes | Finishing, detail work |
Understanding these factors helps in choosing the right lathe and settings for your projects. This ensures that your woodturning is both efficient and precise.
Lathe Accessories: Enhancing Functionality
Lathe accessories are essential for wood turning. They make the job easier and more efficient. These accessories improve the lathe’s functionality and expand its capabilities.
Chucks And Faceplates
Chucks and faceplates are crucial accessories for any wood lathe. They help in holding the wood securely. This allows for accurate and safe turning.
| Accessory | Function |
|---|---|
| Chucks | Hold the wood tightly |
| Faceplates | Attach the wood to the lathe |
There are different types of chucks:
- Scroll chucks: Ideal for holding round objects.
- Four-jaw chucks: Perfect for irregular shapes.
Faceplates come in various sizes. They are used for large pieces.
Specialized Cutting Tools
Specialized cutting tools are vital for intricate designs. They allow for precise cuts and detailed work.
Common specialized cutting tools include:
- Spindle gouges: Best for fine detailing.
- Bowl gouges: Perfect for shaping bowls.
- Parting tools: Used for cutting wood into sections.
Using the right cutting tool is important. It ensures smooth and accurate cuts.

Credit: woodwhirled.com
Safety Features: Protecting The Woodturner
Wood turning can be a fun hobby. But it is also important to be safe. Woodturning lathes come with many safety features. These features protect the woodturner from harm. Let’s explore some key safety features.
Guards And Lockouts
Guards cover moving parts. They keep fingers safe. Guards are usually clear. This allows the woodturner to see their work.
Lockouts prevent the lathe from starting by accident. They are useful during maintenance. A lockout ensures the lathe stays off until you are ready.
Here’s a quick look at common guards and lockouts:
| Feature | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Guard | Protects fingers from moving parts |
| Lockout | Prevents accidental start-up |
Safety Best Practices
Always wear safety goggles. They protect your eyes from dust and wood chips.
Use hearing protection. Lathes can be loud. Earplugs or earmuffs help protect your hearing.
Follow these steps before using a lathe:
- Check that all guards are in place.
- Ensure the workpiece is secure.
- Verify the lathe speed is correct.
Keep your workspace clean. A tidy area reduces accidents.
Always stand to the side when starting the lathe. This keeps you safe if something flies off.
By using these safety features and best practices, you can enjoy wood turning safely.
Maintenance: Keeping Your Lathe In Top Shape
Maintaining your wood turning lathe ensures efficient and safe operation. Regular care extends the life of your machine. It also improves the quality of your work. Below, we outline key maintenance tasks.
Regular Cleaning Routines
Regular cleaning helps prevent wear and tear. Follow these steps for a clean lathe:
- Wipe down the lathe after each use.
- Remove wood shavings and dust from all parts.
- Inspect the tool rest and bed for debris.
- Use a brush to clean hard-to-reach areas.
Use compressed air to blow away fine dust. Clean the spindle and tailstock thoroughly. Lubricate moving parts as needed. This ensures smooth operation and reduces friction.
When To Seek Professional Help
Sometimes, professional help is necessary. Here are signs you need expert assistance:
- Unusual noises during operation.
- Vibration or wobbling of the lathe.
- Difficulty in adjusting parts.
- Visible wear on crucial components.
If any of these issues occur, contact a professional. Regular inspections by experts can prevent major problems. They can also provide specialized maintenance services.
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Wipe down lathe | After each use |
| Remove wood shavings | After each use |
| Inspect tool rest | Weekly |
| Lubricate parts | Monthly |
Keeping your lathe clean and well-maintained ensures it performs at its best. Regular care and professional help can make a big difference.

Credit: www.pinterest.com
Upgrades And Customization: Personalizing Your Lathe
Wood turning lathes are versatile tools. They allow for numerous customizations. Upgrading your lathe can enhance performance. It also makes your work more enjoyable. Personalizing your lathe can also reflect your style. Let’s explore some popular modifications and considerations.
Popular Modifications
Many woodturners love to modify their lathes. Here are some popular modifications:
- Tool Rests: Upgrading to a curved or modular tool rest can improve precision.
- Spindle Locks: Installing a spindle lock makes changing accessories easier.
- Lighting: Adding adjustable lighting enhances visibility during intricate work.
- Variable Speed Controls: A variable speed control allows for more precise adjustments.
- Tailstock Upgrades: A quick-release tailstock saves time and increases efficiency.
Compatibility And Considerations
Before making any upgrades, consider compatibility. Not all parts fit every lathe. Check the manufacturer’s guidelines first.
Budget: Upgrades can vary in cost. Plan your budget accordingly.
Skill Level: Some upgrades require technical skills. Ensure you are comfortable with the installation.
Frequency of Use: Consider how often you use your lathe. Frequent users may benefit more from high-end upgrades.
Here’s a table to summarize key considerations:
| Consideration | Details |
|---|---|
| Compatibility | Check if the part fits your lathe model. |
| Budget | Plan your expenses based on upgrade costs. |
| Skill Level | Ensure you have the skills for installation. |
| Frequency of Use | Frequent users benefit more from upgrades. |
Upgrading and customizing your wood turning lathe can be rewarding. It enhances your woodworking experience and makes your lathe unique.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Parts Of A Wood Lathe Called?
A wood lathe consists of several key parts: the headstock, tailstock, tool rest, bed, and spindle.
What Are The 5 Major Parts Of The Lathe Machine?
The five major parts of a lathe machine are the bed, headstock, tailstock, carriage, and spindle.
How Do I Identify Wood Lathe Tools?
Identify wood lathe tools by their specific shapes and functions. Common tools include gouges, chisels, parting tools, and scrapers. Check handles for labels or markings indicating their type.
What Is The Best Wood For Turning On Lathe?
The best wood for turning on a lathe includes hardwoods like maple, cherry, and walnut. These woods offer fine grain and stability.
Conclusion
Mastering wood turning lathe parts enhances your woodworking skills. Quality components ensure precision and durability. Investing in reliable parts boosts your projects’ success. Maintain your lathe well for optimal performance. Embrace the art of woodturning with confidence and creativity. Happy turning!