Table of Contents
Turning tools for metal are essential in machining operations. They shape and finish metal parts with precision.
Turning tools play a crucial role in the metalworking industry. They help machinists create accurate and high-quality metal components. These tools come in various shapes and sizes, each designed for specific tasks. Carbide, high-speed steel, and ceramic are common materials used to make turning tools.
Quality turning tools ensure efficient cutting and longer tool life. Proper selection and maintenance of these tools can significantly enhance machining performance. Investing in the right turning tools can lead to better productivity and cost savings. Understanding the types and uses of turning tools is essential for anyone involved in metalworking.
Introduction To Metal Turning Tools
Metal turning tools are used to shape metal. They cut and carve the metal piece. This process makes the metal smoother. Turning is very important in metalwork. It creates precise shapes and sizes. Lathes are often used in turning. These machines spin the metal. The tools then cut it to the desired shape.
There are many types of turning tools. Roughing tools remove large chunks of metal. Finishing tools make the metal smooth. Parting tools cut off parts of the metal piece. Threading tools create threads on the metal. Boring tools make holes in the metal. Each tool has a special job. They help create perfect metal pieces.

Credit: www.penntoolco.com
Material Choices For Turning Tools
High-Speed Steel (HSS) is tough and can handle heavy use. It is cheaper than carbide. HSS can be sharpened many times. It is best for low-speed cutting. Carbide is harder and stays sharp longer. It works well at high speeds. Carbide is more expensive than HSS. Each material has its own best uses.
To choose the right material, think about the job. For rough cutting, HSS is a good choice. For smooth and fast cuts, use carbide. Think about your budget too. HSS is cheaper and good for many jobs. Carbide lasts longer but costs more. Pick the material that fits your needs best.
Tool Geometry And Its Impact On Turning
Rake angles help with chip removal. Positive rake angles reduce cutting forces. Negative rake angles make tools stronger. Relief angles prevent rubbing on the workpiece. This reduces tool wear. Clearance angles ensure smooth cutting action. Each angle affects the cutting process differently. Choosing the right angles is crucial for effective turning.
Tool point geometry affects cutting efficiency. A sharp point reduces cutting resistance. A rounded point increases tool life. The tool’s shape affects heat dissipation. Proper geometry enhances surface finish. Choosing the right tool point is key for quality results. Pay attention to tool geometry for optimal performance.
Sharpening Techniques For Precision
Sharpen tools on a stable surface. Use a fine-grit stone for the best results. Keep the sharpening angle consistent. Dip the tool in water to cool it. Always sharpen in one direction. Clean the tool after sharpening. This ensures no metal bits remain.
Check the tool edge regularly. A dull edge can cause problems. Use a strop to maintain the edge. Avoid overheating the tool. This can damage the metal. Store tools in a dry place. Moisture can cause rust.
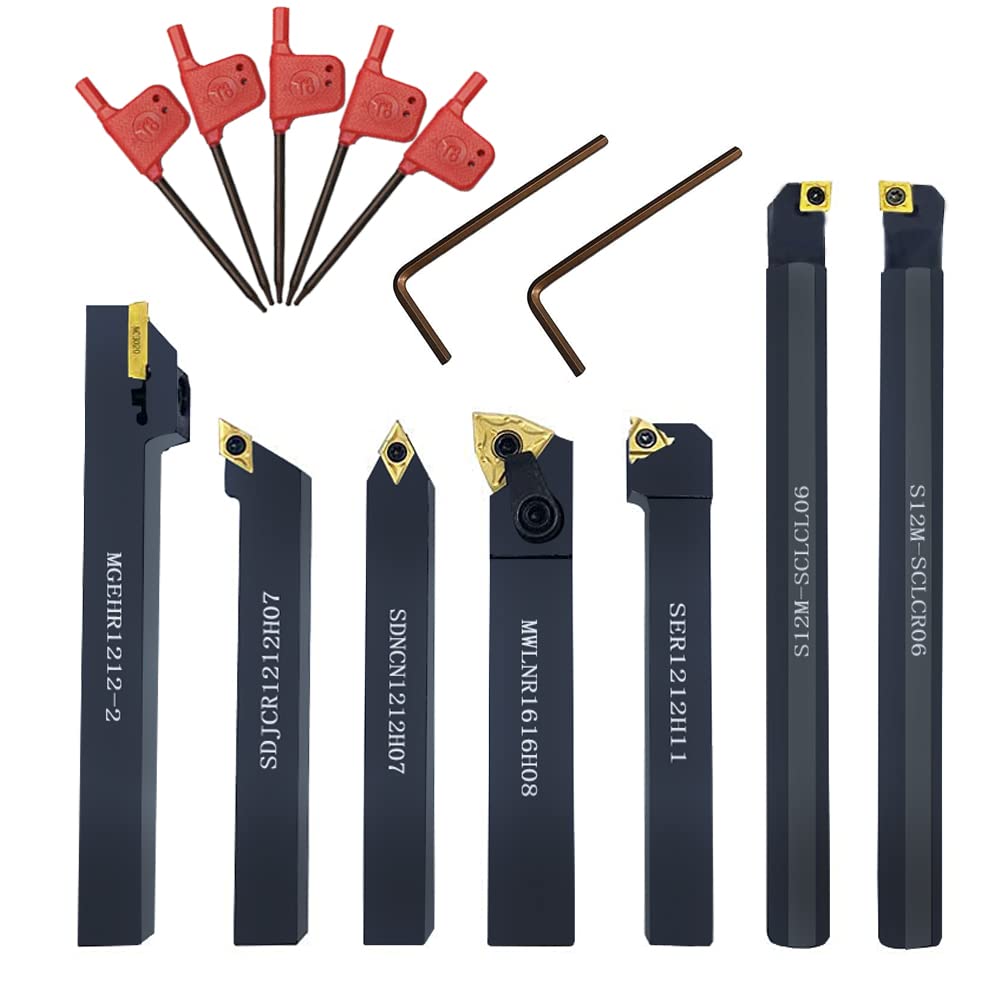
Toolholding And Stability
The toolholder is very important for machining. It affects the stability and accuracy of the tool. Always use a high-quality toolholder. This helps to reduce vibrations and improve tool life. Select the toolholder that matches the tool and the machine. This will ensure better performance and results.
Vibration can damage tools and parts. Use damping materials to absorb vibrations. Tighten all connections to prevent movement. Balance the tool and workpiece. This will help in reducing vibration. Using shorter toolholders can also help. Always check for worn-out parts and replace them.
Speeds, Feeds, And Depth Of Cut
Using the right cutting parameters is key. The right speed improves tool life. Feed rate affects the surface finish. Depth of cut impacts the overall machining time. Each parameter must be balanced for the best results.
High speeds can lead to better finishes. But, too high a speed can damage the tool. Slower speeds may extend tool life. Adjusting the speed helps achieve the best finish quality.
Coolant Use In Metal Turning
There are different types of coolants for metal turning. Water-based coolants are common. They are good for heat reduction. Oil-based coolants give better lubrication. They help in heavy-duty cutting. Synthetic coolants are chemical-based. They are used for high-speed operations. Semi-synthetic coolants combine water and oil properties. They balance cooling and lubrication.
Coolant application is very important. Flood cooling is the most common method. It covers the cutting area with coolant. Mist cooling sprays fine droplets of coolant. It is good for small parts. High-pressure cooling uses strong coolant jets. It helps in deep cuts. Through-tool cooling delivers coolant through the tool. It reaches hard-to-access areas.
Advanced Turning Techniques
Master advanced turning techniques with high-precision metal turning tools. Achieve exceptional accuracy and smooth finishes on complex parts. Enhance productivity and craftsmanship in your machining projects.
Introduction To Thread Turning
Thread turning creates screw threads on metal pieces. This technique is essential for fasteners and machine parts. Using the right tool ensures accuracy and smooth threads. Proper setup prevents errors and damages. Always maintain sharp tools for clean cuts. Adjust the speed and feed for different metals. Practice improves precision and skill.
Mastering Complex Shapes And Tapers
Creating complex shapes and tapers needs skill. Start with basic shapes to build confidence. Use templates for consistency. Adjust the lathe angle for different tapers. Use fine cuts for smooth surfaces. Measure often to ensure accuracy. Practice helps in mastering these techniques. Different metals require unique approaches. Keep tools sharp for best results.
Troubleshooting Common Turning Issues
Tool wear can cause many problems. Dull tools leave rough surfaces. Always check the tool’s edge. Replace it if needed. Use a microscope for close inspection. Monitor the cutting speed. High speed increases wear. Use coolant to reduce heat. Heat speeds up wear. Check alignment. Misaligned tools wear out fast.
Precision is key in turning. A worn tool affects precision. Tighten all machine parts. Loose parts cause vibration. Vibration ruins precision. Measure the workpiece often. Adjust as needed. Surface finish issues are common too. Use a sharp tool for a smooth finish. Reduce cutting speed for better results.
Safety Precautions For Turning Operations
Ensure the correct setup of turning tools to prevent accidents during metalworking. Always wear safety gear and regularly check equipment for wear and tear.
Personal Protective Equipment
Always wear safety goggles to protect your eyes. Use ear protection to guard against loud noises. Wear gloves to protect your hands from sharp tools. Steel-toed boots are essential for foot safety. A face shield can add extra protection. Make sure you have a fire extinguisher nearby.
Safe Handling And Storage Of Tools
Store tools in a dry and clean place. Keep tools away from edges to prevent falls. Use tool holders for sharp tools. Ensure all tools are properly labeled. Always clean tools after use. Check tools for damage regularly. Ensure tools are securely fastened before use. Organize tools for easy access.
The Future Of Metal Turning
New tool technology is changing metal turning. Advanced materials make tools last longer. These tools cut metal faster and more precisely. Coatings on tools reduce wear and tear. This means tools stay sharp for a longer time. Smart tools now have sensors. These sensors help in monitoring the cutting process. Better designs also improve how tools perform.
Automation is making metal turning easier. Robots can now handle many tasks. This reduces the need for human workers. Machines can work 24/7 without breaks. This boosts production rates. Computer systems help in controlling the machines. These systems ensure precise and consistent results. Safety also improves with automation. Less human involvement means fewer accidents.

Credit: www.amazon.com

Credit: bigeasymart.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Best Steel For Turning Tools?
High-speed steel (HSS) is the best for turning tools. It offers excellent toughness and maintains sharpness.
What Is The Best Metal For Lathe Tools?
High-speed steel (HSS) is the best metal for lathe tools. It offers durability, heat resistance, and sharp cutting edges.
What Are Turning Tools Made Of?
Turning tools are made of high-speed steel, carbide, ceramics, and cubic boron nitride for durability and precision in machining.
What Are The Common Metal Lathe Tools?
Common metal lathe tools include turning tools, boring bars, parting tools, threading tools, and knurling tools. These tools shape and finish metal workpieces efficiently. Using the right tools ensures precision and quality in metalworking projects.
Conclusion
Mastering the use of turning tools in metalworking boosts efficiency and precision. Invest in quality tools to enhance your projects. Regular maintenance ensures longevity and optimal performance. Stay updated with the latest techniques for the best results. Happy machining!